ILLUMINA SEQUENCING - THE BASIS OF NEXT GENERATION SEQUENCING :-
HEREDITY HEALTHCARE AND LIFE SCIENCES
Contact us:
Dr.Gopal Purohit
Email:gopal.purohit@hdls.in
Contact number:7381298980
Website: www.heredity.in
Written by: SAPTARSHI BHATTACHARYYA
In principle, the concept behind NGS technology is similar to CE
sequencing. DNA polymerase catalyzes the incorporation offluorescently
labeled deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs) into a DNA template strand
during sequential cycles ofDNA synthesis. During each cycle, at the point of
incorporation, the nucleotides are identified by fluorophore excitation.
Thecritical difference is that, instead of sequencing a single DNA fragment,
NGS extends this process across millions of fragmentsin a massively parallel
fashion. More than 90% of the world's sequencing data are generated by Illumina
sequencing bysynthesis (SBS) chemistry.
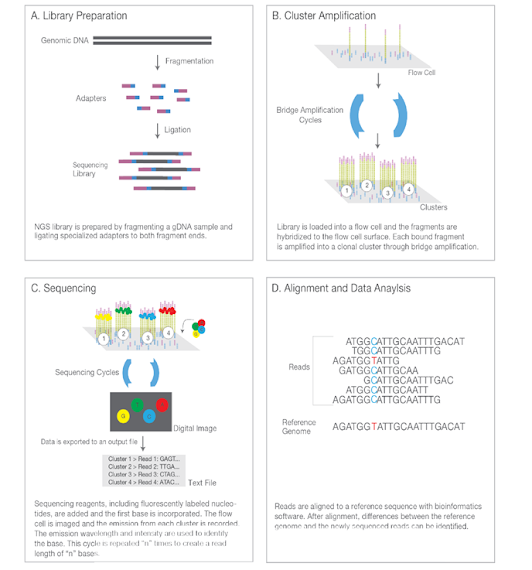
Illumina NGS workflows include four basic steps:
1. Library Preparation—The sequencing library is prepared by
random fragmentation of the DNA or cDNA sample, followedby 5′and
3′adapter ligation. Alternatively, “tagmentation” combines the
fragmentation and ligation reactions into a single step that greatly increases the efficiency of the
library preparation process.Adapter-ligated fragments arethen PCR amplified and
gel purified.
2. Cluster Generation—For cluster generation, the library is loaded into a flow cell where fragments are captured on a lawn ofsurface-bound oligos complementary to the library adapters. Each fragment is then amplified into distinct, clonal clustersthrough bridge amplification. When cluster generation is complete, the templates are ready for sequencing.
3. Sequencing—Illumina SBS technology uses a proprietary reversible terminator–based method that detects single basesas they are incorporated into DNA template strands. As all four reversible terminator–bound dNTPs arepresent during each sequencing cycle, natural competition minimizes incorporation bias and greatly reduces raw errorrates compared to other technologies.The result is highly accurate base-by-base sequencing that virtually eliminatessequence context–specific errors, even within repetitive sequence regions and homopolymers.
4.Data Analysis—During data analysis and alignment, the newly identified sequence reads are aligned to a referencegenome. Following alignment,many variations of analysis are possible, such as single nucleotidepolymorphism (SNP) or insertion-deletion (indel) identification, read counting for RNA methods, phylogenetic ormetagenomic analysis, and more





Comments
Post a Comment